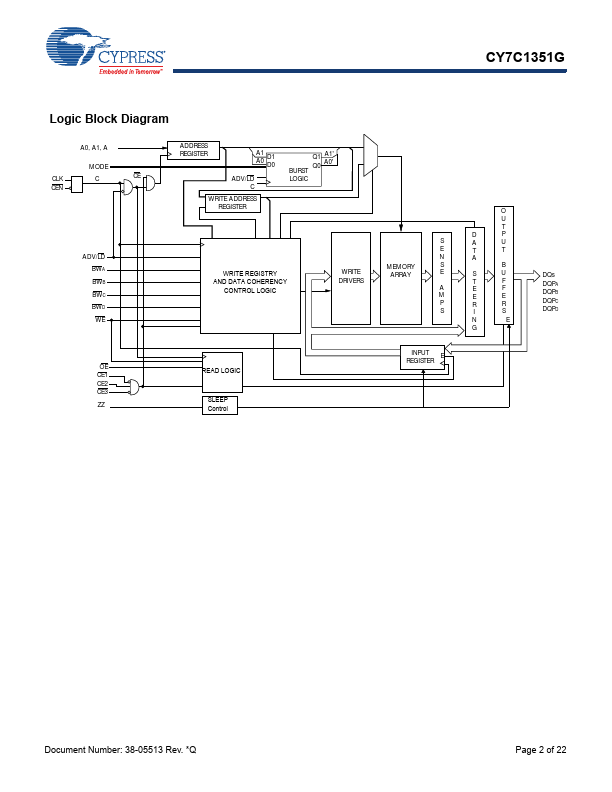
CY7C1351G Description
The CY7C1351G is a 3.3 V, 128K × 36 synchronous flow-through burst SRAM designed specifically to support unlimited tru.
CY7C1351G Key Features
- Can support up to 133-MHz bus operations with zero wait states
- Data is transferred on every clock
- Pin patible and functionally equivalent to ZBT™ devices
- Internally self-timed output buffer control to eliminate the need
- Registered inputs for flow-through operation
- Byte write capability
- 128 K × 36 mon I/O architecture
- 2.5 V/3.3 V I/O power supply (VDDQ)
- Fast clock-to-output times
- 6.5 ns (for 133-MHz device)